A Nitrogen is a part of the amino functional group which is a component of both proteins and nucleic acids.
Protein is made up of amino acid monomers [subunits that can join together to form more complex structures] which all have this amino functional group included in their structure. The nitrogen in this functional group that helps to form polypeptide bonds with other amino acids in order to form proteins. Polypeptide bonds are what ‘hold together’ proteins. So essentially, nitrogen helps form proteins by aiding in the bonding amino acids.
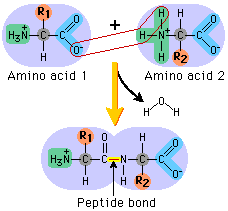 |
| https://thebiochemeffect.wordpress.com/tag/peptide-bonds/ |
Nitrogen bases In nucleic acids make up the code in DNA and RNA. There are five nitrogen bases, adenine, guanine, uracil, thymine, and cytosine. Thymine only appears in DNA, and uracil appears only in RNA. DNA and RNA dictate how an organism is built and constructed. So Nitrogen plays a very important part in nucleic acids.
 |
| https://biochemaholic.wordpress.com/ |
No comments:
Post a Comment